With the introduction of more and more IOT and embedded devices in the market, hackers are starting to find firmware exploitation as a more viable mechanism for gaining access into networks and taking over machines. Many of these devices don’t include security mechanisms out of the box, can contain backdoors that provide easy shells, or contain a number of other vulnerabilities that can make them an easy point of entry into any network.
This blog will be the first in a series on how to dump and analyze the firmware of embedded devices. I will address the various ways we can access firmware and analyze it for vulnerabilities so we can confirm if these connected devices that are so prevalent in all our homes are really safe and secure.
The Badge Challenge
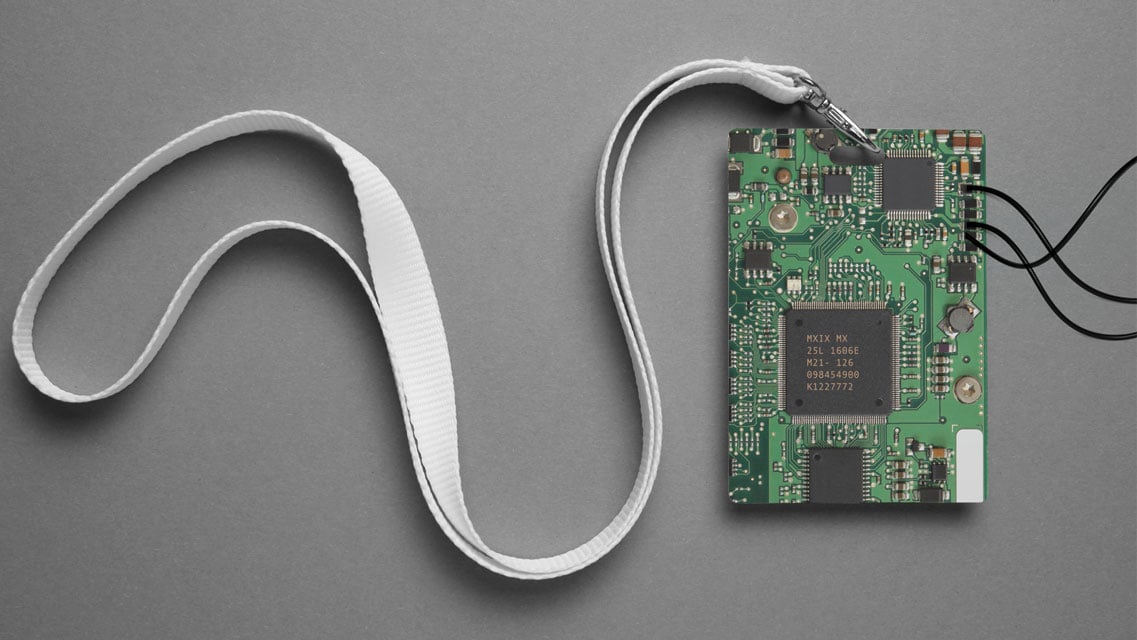
The first device we will be looking at is a conference badge. I got the idea from the badge challenge from a BSides Rochester event (fig.1). A badge challenge, for those who don’t know, is often done at security conferences where an electronic badge is provided to attendees. Because of its very nature, these badges house sensitive data and the challenge is around finding vulnerabilities and data that can assist in the conference’s overall “Capture the Flag” hacking competition.
If you’ve never attended a BSides conference I recommend looking at one near you (http://www.securitybsides.com/w/page/12194156/FrontPage).

Figure 1 – bsides Badge
The first thing we need to do when analyzing an embedded device – like this badge — is to identify the chips on the board. Generally, what we are trying to find is some sort of chip that stores the data for the firmware. You can think of this as a hard drive of sorts. Often this is a flash chip or an MCU (microcontroller unit). This chip is used for storing data and usually contains the bootloader, kernel, and filesystem for the device. If we find the flash chip, we can access it and dump its contents and the firmware.
Fortunately, this device makes it pretty easy, as this device only has 1 chip on the board (everything else is an LED).
What we want to do next is identify the type of chip this is. All chips will have writing on top of them that identifies the make and model of the chip. The writing can often be illegible to the naked eye, so using your phone’s camera and zoom features or a magnifying glass will help ease this process.
This chip has “Atmel 10v Tiny 85V” (fig.2) which signifies we are working with an MCU. Googling this provides us with a valid data sheet for our chip: https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/Atmel-2586-AVR-8-bit-Microcontroller-ATtiny25-ATtiny45-ATtiny85_Datasheet.pdf which we will use to identify the pins we need to connect to (fig.3).

Figure 2 – bsides Badge Back
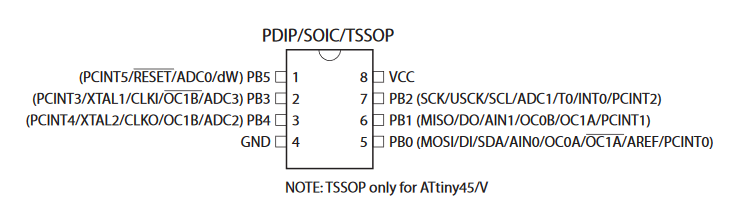
Figure 3 – atiny85 Diagram
Here we can see what each pin does relative to the Atmel chip. The little circle at the top left of the chip identifies the orientation and tells us where pin 1 is. At this point it’s time to connect our Bus Pirate to the Atmel chip. I will use a SOIC clip to simplify the connection.
To connect the SOIC clip, make sure the side with the red line is on the side of the chip with the circle in the top left. This will align the 1-8 pins together on the SOIC clip perfectly. In addition, make sure the metal contacts on the clip touch the metal contacts on the pin. If done properly, we can identify the pinouts on the clip by looking at the numbers on the end.
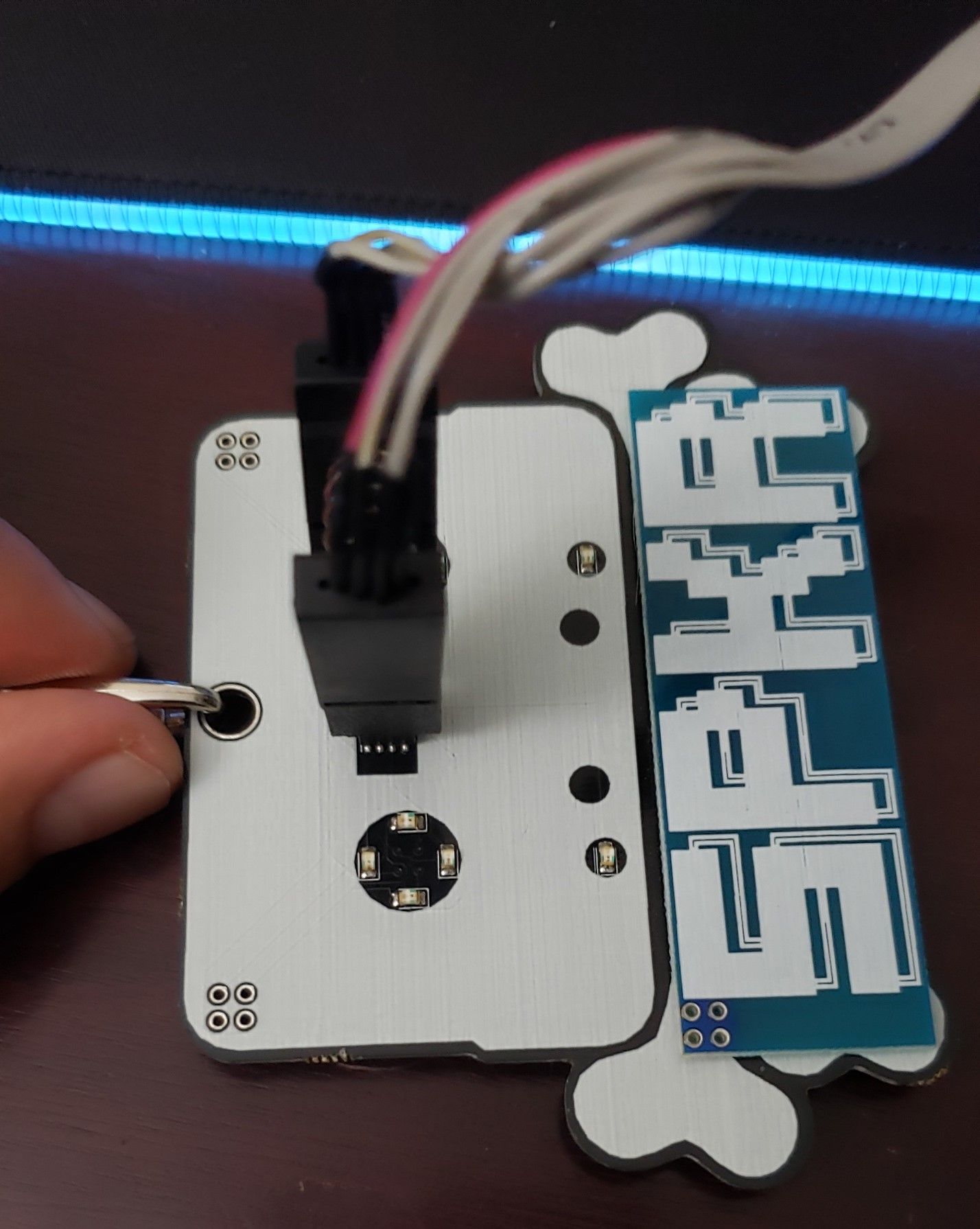

Figure 4 – Speaker Badge Connected to Soic Clip
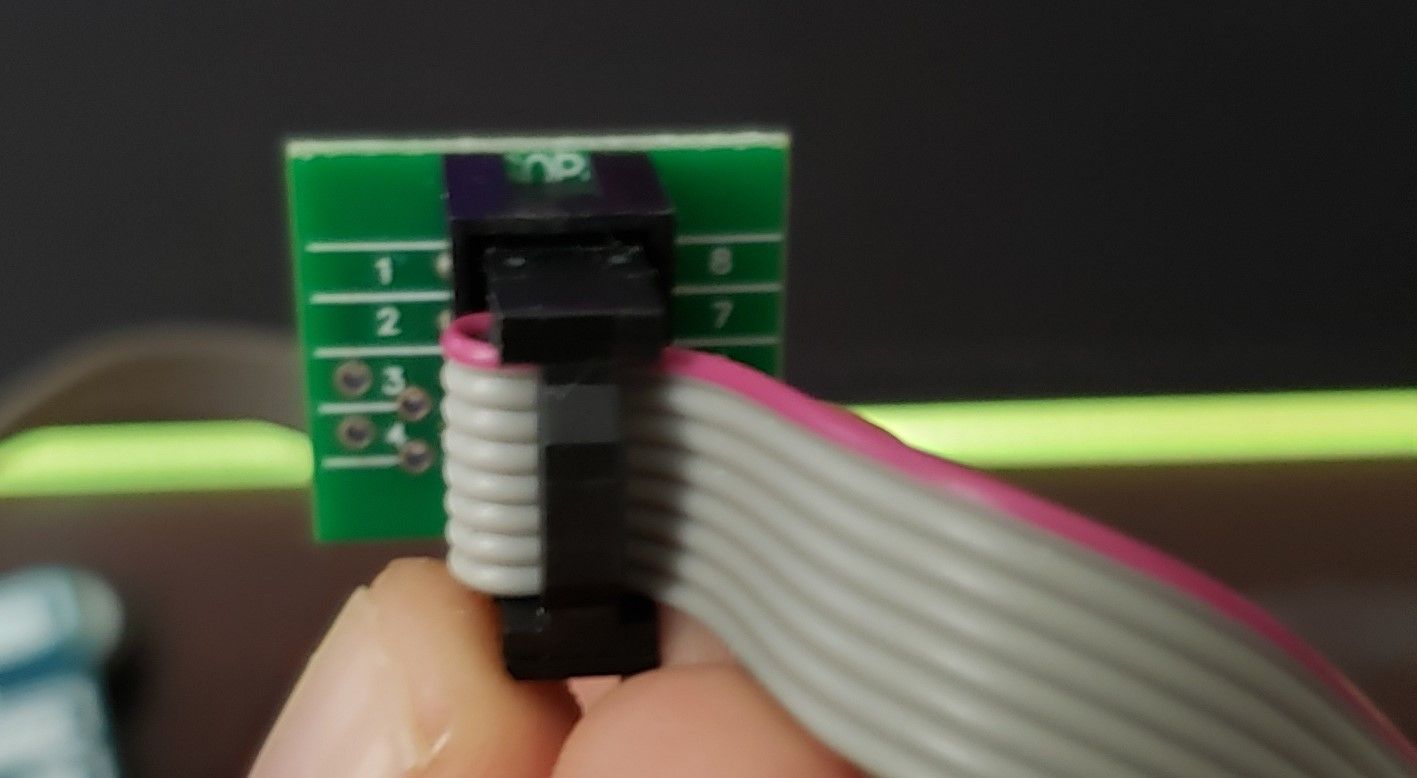
Figure 5 – Soic Clip
Now that the SOIC clip is attached we just need to connect the Bus Pirate to the SOIC clip and dump the data on the chip. Connect the pins based on the table below.
| Atmel | Bus Pirate |
|---|---|
| Reset | CS |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3v |
| SCK | CLK |
| MISO | MISO |
| MOSI | MOSI |
This is what it looks like with the pins connected:
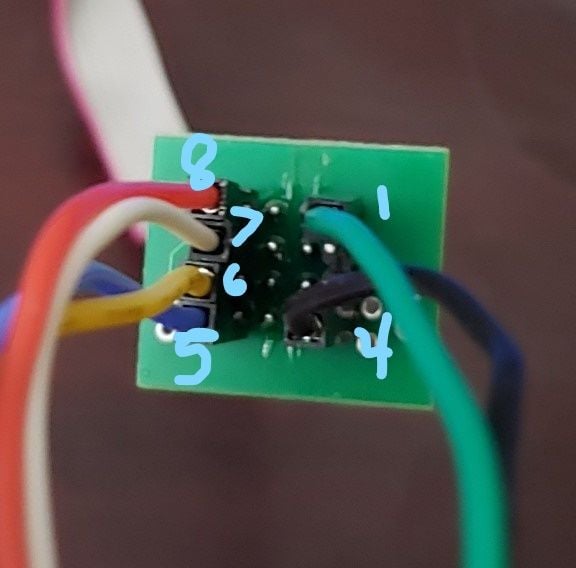
Figure 6 – Soic Clip Labeled
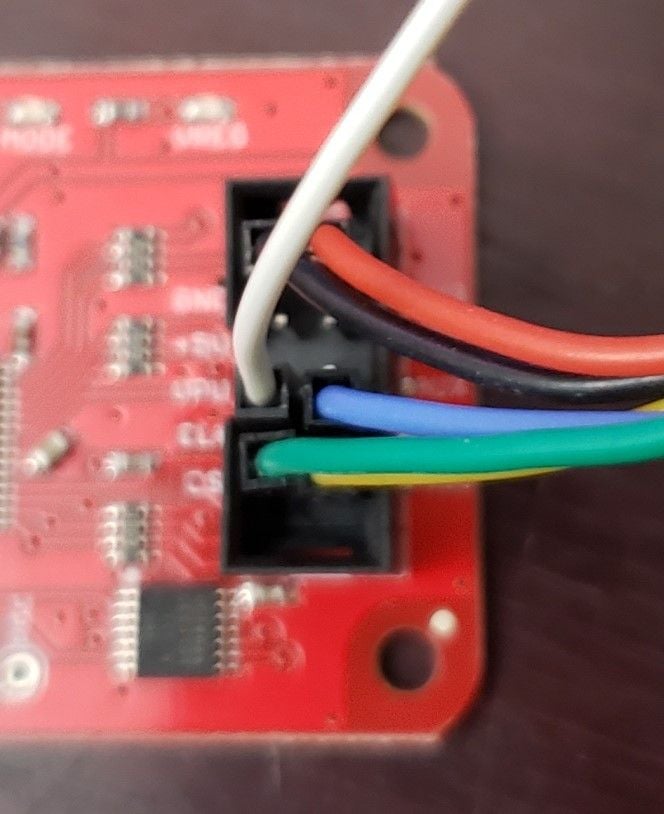
Figure 7 – Bus Pirate Cables
Now we connect the Bus Pirate to our machine and dump the firmware using avrdude software. Each cable is a totally different color to make it easy to distinguish. Fig.6 shows the SOIC Clip end connection and fig.7 shows the connection into the Bus Pirate. For the actual dumping, I personally like using Ubuntu and Attify (https://github.com/adi0x90/attifyos) VMs for this sort of work. The Attify VM often works if the Ubuntu VM fails and vice versa.
The following command will list all chips avrdude supports: “avrdude -p ?”
Within the results we will look for our chip, specifically to see if it supports Tiny85, which it does.
| T45 | = ATiny45 |
| T461 | = ATiny461 |
| T5 | = ATiny5 |
| T84 | = ATiny84 |
| T85 | = ATiny85 |
| T861 | = ATiny861 |
| T88 | = ATiny88 |
| T9 | = ATiny9 |
| X128a1 | = ATxmega128A1 |
And using this final command we can dump the firmware to a file flash.bin: “sudo avrdude -p attiny85 -c buspirate -P /dev/ttyUSB0 -U flash:r:flash.bin:r”
Now at this point, I had issues recreating this for screenshots and discovered at some point I burned both the CS and MISO pins on my Bus Pirate so I am unable to continue dumping until my new device arrives. Lesson here is, be careful with your dumping devices — especially the more expensive ones like the Jtagulator. If you don’t plug things in correctly you run a real risk of burning your devices.
To test the old Bus Pirate we connect the 5v pin to the VPU pin and the 3.3v pin to the ADC pin (fig.8):
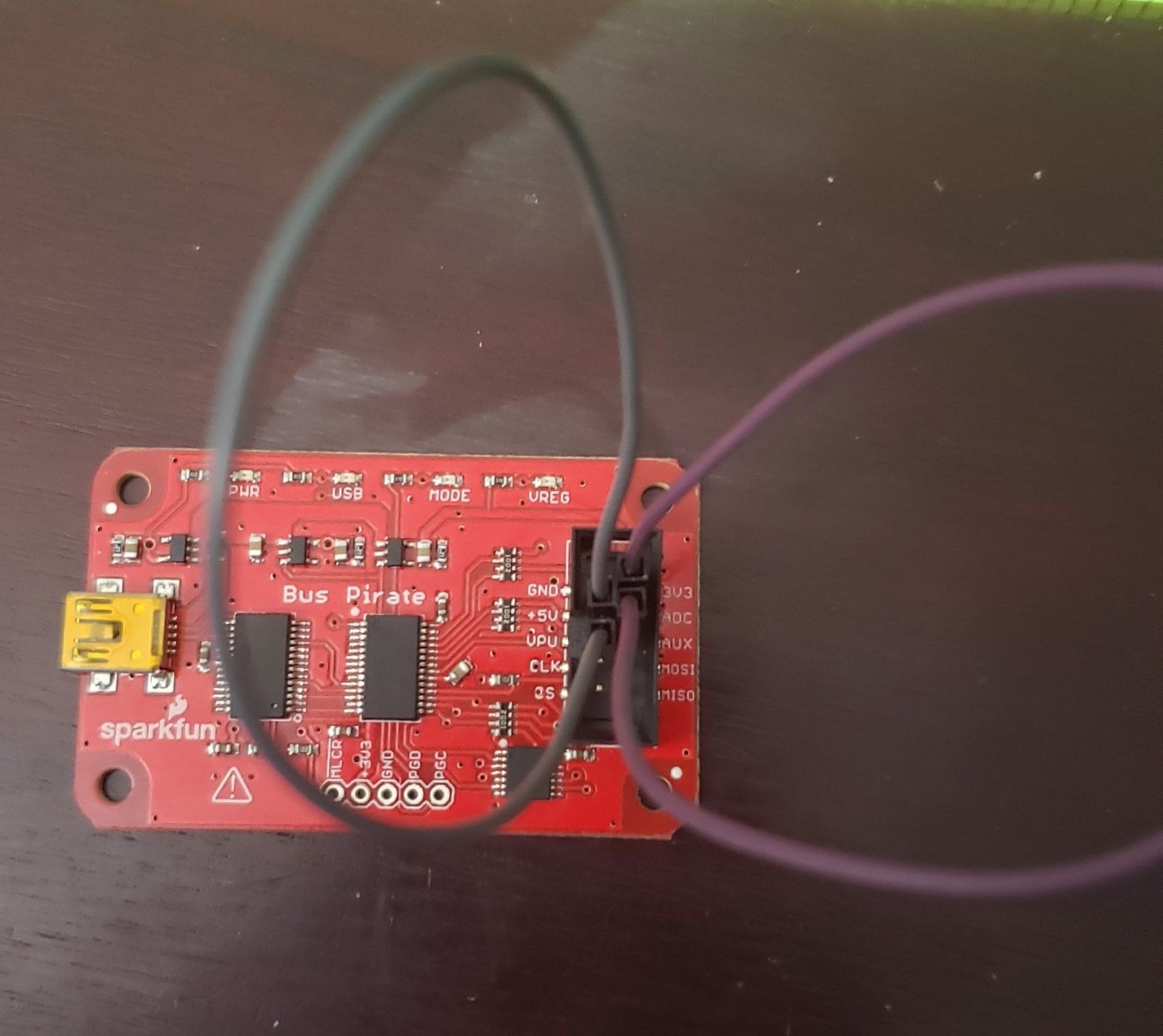
Figure 8 – Bus Pirate Cables Test
Then we connect the Bus Pirate to our machine and connect into it with the following command: “sudo picocom -b 115200 -r -l /dev/ttyUSB0”
You can start a test by entering “~” and then hitting space. Then, if anything fails in the results there may be something wrong with your device. I tried flashing several different firmwares to see if that would resolve anything but, in reality, I just wasn’t very careful with this device as it was pretty cheap, and I most likely burned the pins. As you can see below, my CS and MISO pins are failing:
HiZ>~ Disconnect any devices Connect (Vpu to +5V) and (ADC to +3.3V) Space to continue Ctrl AUX OK MODE LED OK PULLUP H OK PULLUP L OK VREG OK ADC and supply 5V(4.92) OK VPU(4.93) OK 3.3V(3.28) OK ADC(3.28) OK Bus high MOSI OK CLK OK MISO FAIL CS OK Bus Hi-Z 0 MOSI OK CLK OK MISO OK CS FAIL Bus Hi-Z 1 MOSI OK CLK OK MISO FAIL CS OK MODE and VREG LEDs should be on! Any key to exit Found 3 errors.
If the firmware dump fails but your Bus Pirate self-tests show everything is OK, it may be the length of the jumper cables, as they can be too long it which will cause connection issues. Using the jumper cables that came with my Jtagulator seem to work fine and haven’t failed me yet.
Luckily, I managed to snag some screenshots of a successful dump before my Bus Pirate burned out on me, you can see these below:
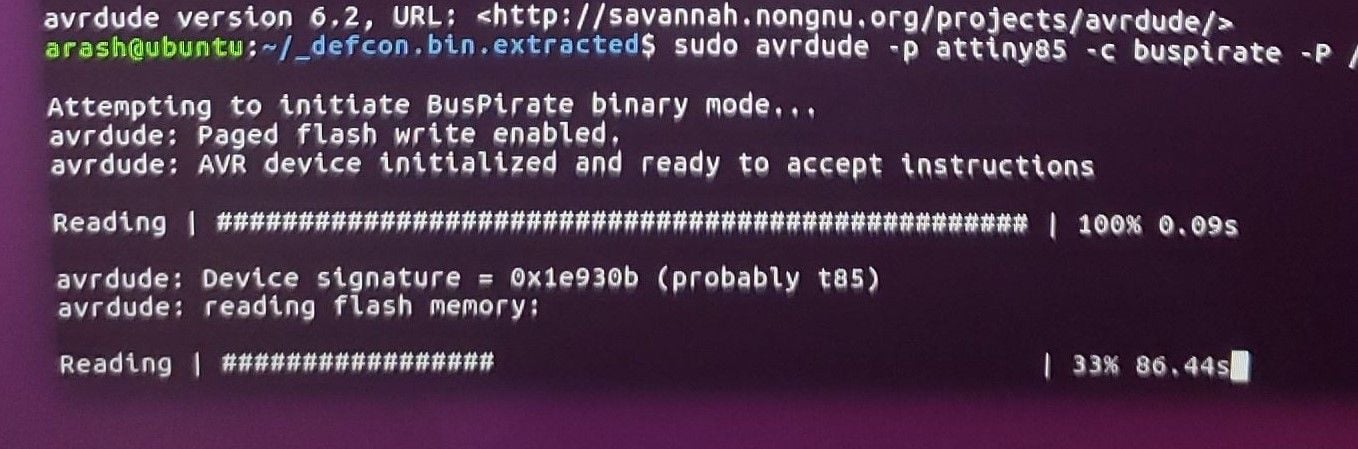
Figure 9 – avrdude Dump
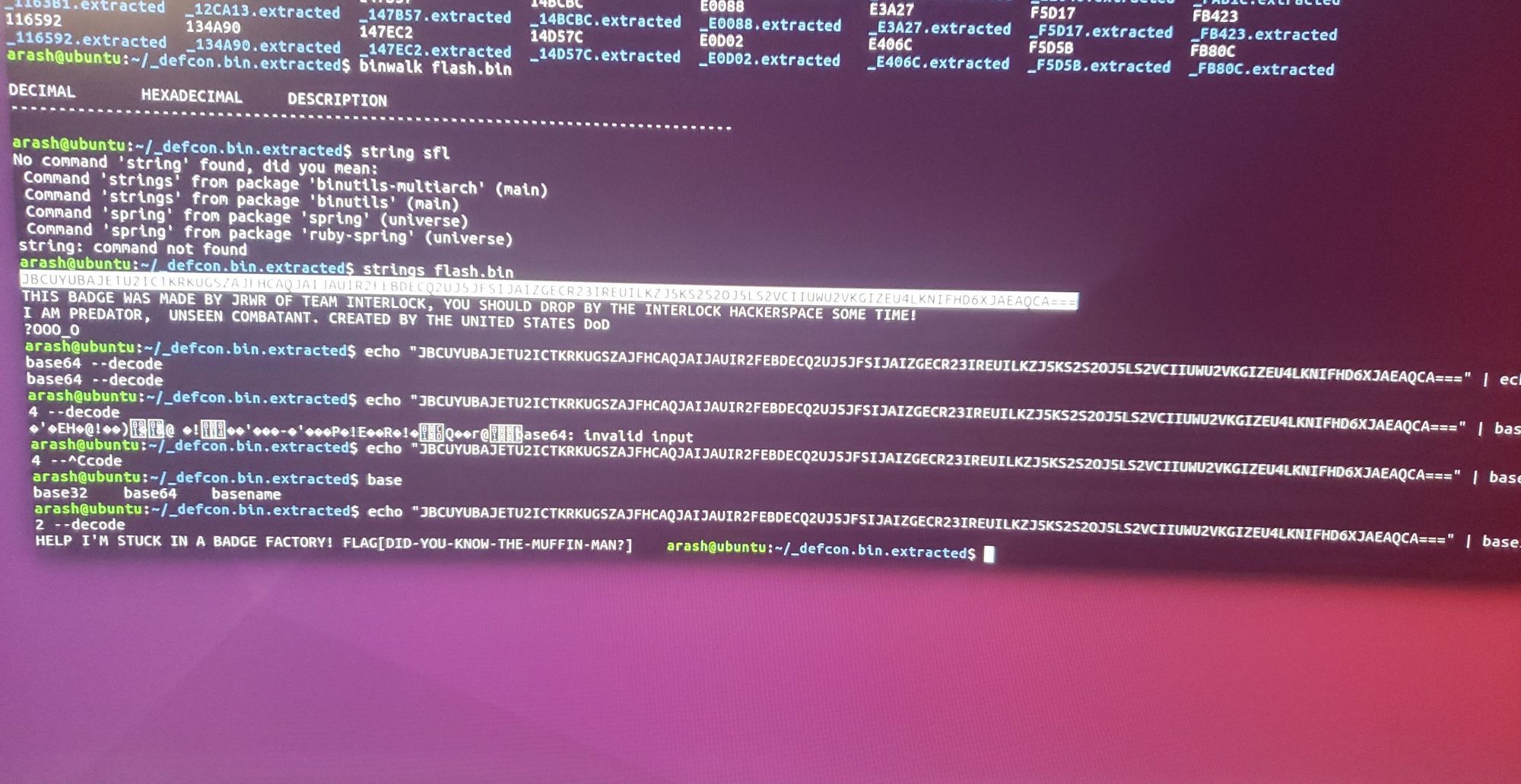
Figure 10 – avrdude Flag
And there’s our flag and badge challenge completed (fig.10)!
Now it’s important to note that in this case, our dump with avrdude only worked because the Atmel chip itself was not locked. It is trivial to lock an Atmel chip by setting what are called “lock bits” after programming the chip. When lock bits are set, and someone tries to dump the chip, it blocks unauthorized access and does not produce any valid firmware data to analyze.
Now that we’ve dumped a simple Atmel chip, we’ll go ahead and dump a more complex board as well.
Dumping a Belkin N300 Router
The next board we will be dumping is a Belkin N300 router. Belkin is one of the most popular consumer router brands, which means unlike the previous CTF Badge, this challenge provides more of a real-world scenario. Discovering an exploit in here could impact households all over the globe.
First thing we’ll do is go ahead and try to locate a flash chip again. This time we identify an MX25L1606E chip (fig.11) (Data Sheet – https://www.macronix.com/Lists/ApplicationNote/Attachments/1991/AN0055V4-Migrate_to_MX25L1606E_and_MX25L8006E-0118.pdf).

Figure 11 – mx25l1606e Chip
Moving forward we’ll use the Attify Badge (fig.12) to dump our firmware since the Bus Pirate is out of commission.
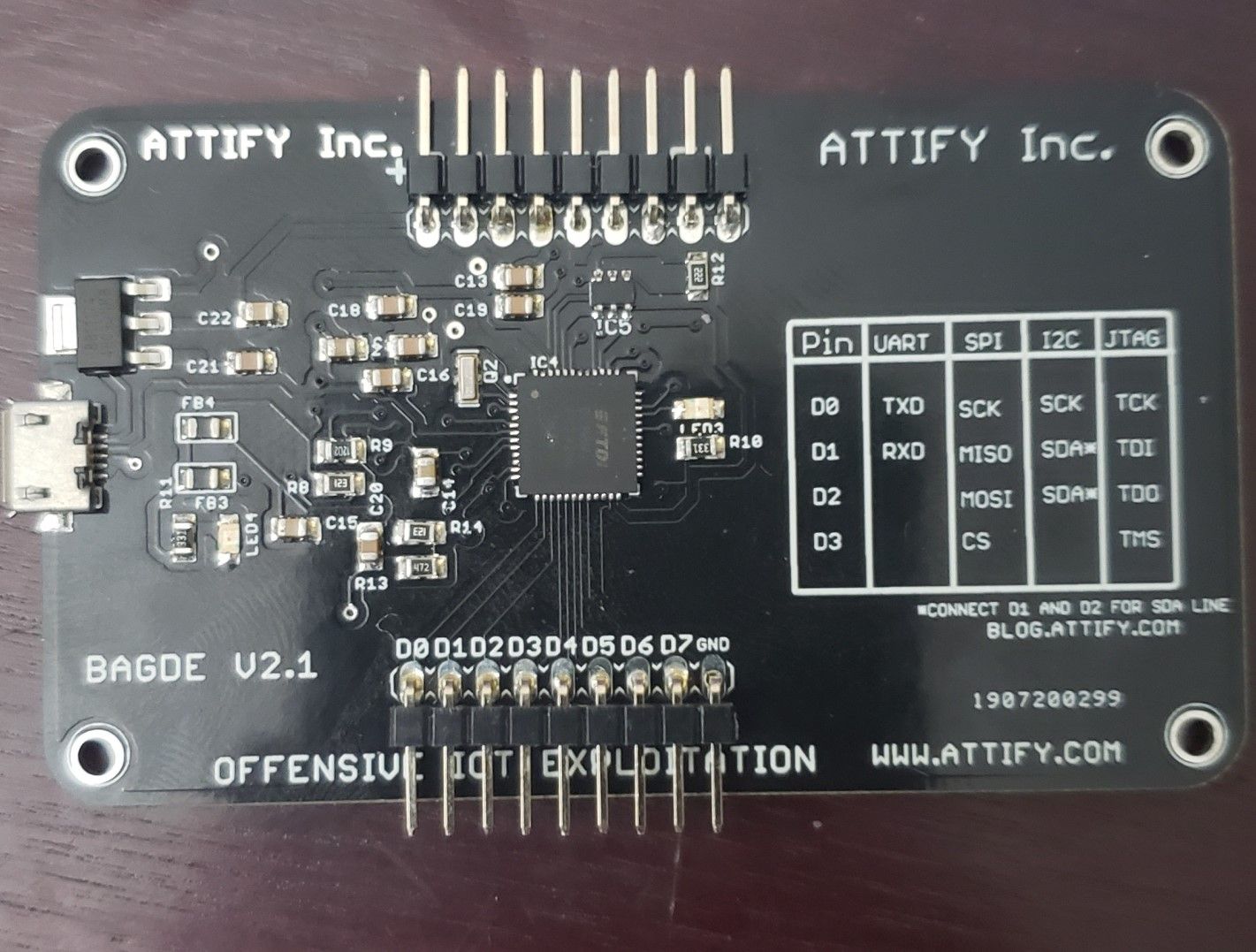
Figure 12 – Attify Badge
The pin out is as follows:
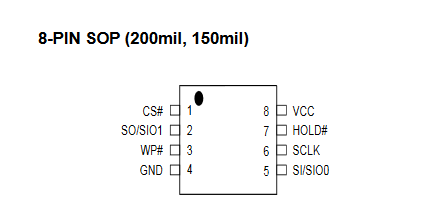
Figure 13 – mx25l1606e Diagram
| MX25L1606E | Attify Badge |
|---|---|
| CS | CS |
| SO | MOSI |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
| SCLK | SCK |
| SI | MOSI |
When completed it should look like this:
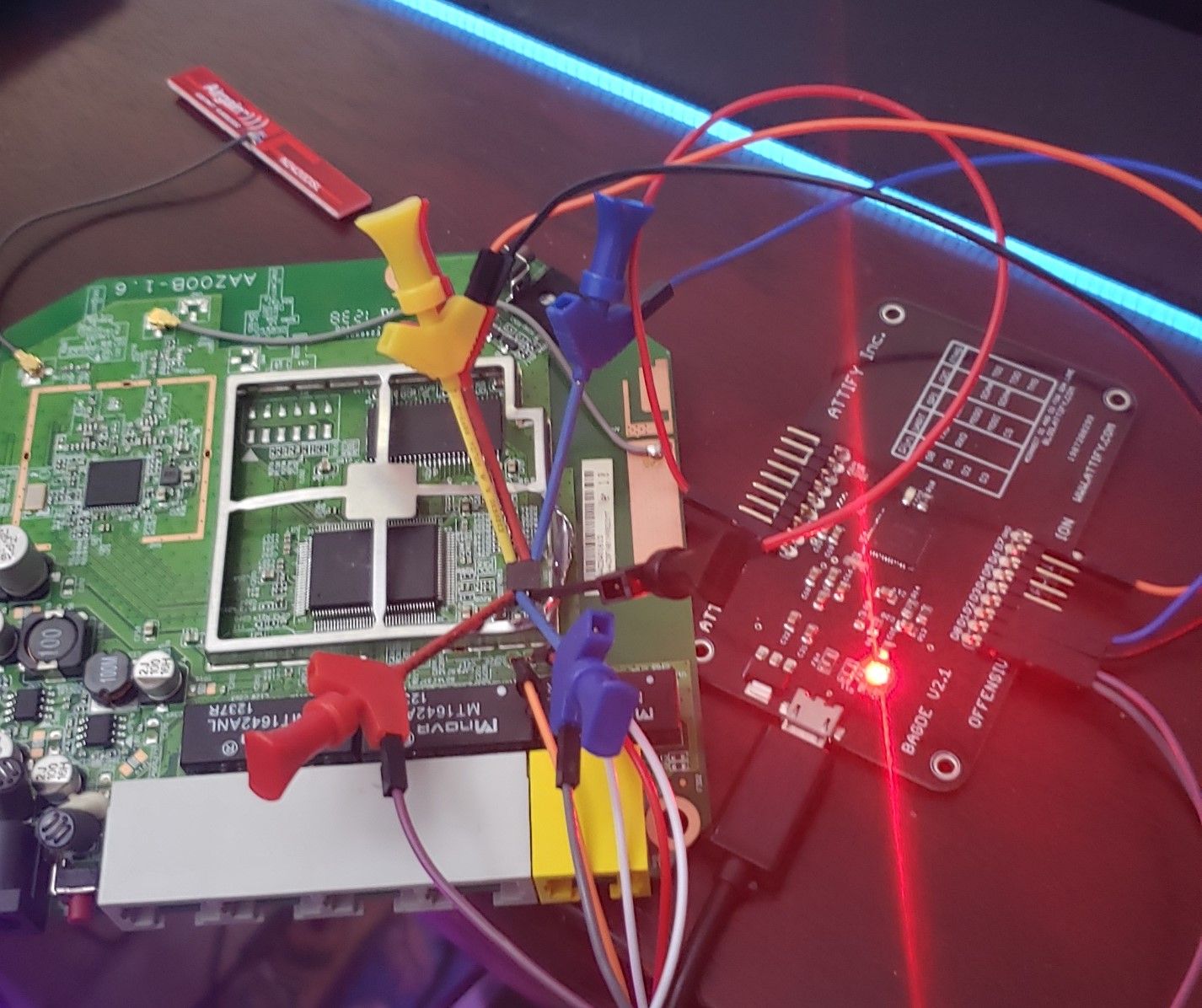
Figure 14 – mx25l1606E -connected to Attify Badge
There was limited space on this board to use a SOIC clip because of the metal frame around the flash chip, as a result I resorted to using alligator clips this round. You can see I had to beat up the framing just to fit the alligator clips even.
Now we’re ready to go ahead and dump this firmware. This time we will be using a utility called “flashrom” instead of avrdude as we will be dealing with a flash SPI chip instead of an Atmel chip.
First we can go ahead and identify if flashrom can dump our chip with the following command: “flashrom -p ft2232_spi:type=232H”
This will attempt to automatically identify our chip. If you are using the Bus Pirate you can just replace the argument passed to -p with the following instead: “flashrom -p buspirate_spi:dev=/dev/ttyUSB0”
/dev/ttyUSB0 is the serial port the Bus Pirate is connected to, change this as required. After running the command it successfully returns the following:
flashrom v0.9.9-r1954 on Linux 4.15.0-88-generic (x86_64) flashrom is free software, get the source code at https://flashrom.org Calibrating delay loop... delay loop is unreliable, trying to continue OK. Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L1605A/MX25L1606E/MX25L1608E" (2048 kB, SPI) on ft2232_spi.
If chip identification fails don’t worry, you can just use “flashrom -L” to find your chip in the list manually and run the next command to see if it will still read the chip: “flashrom -p ft2232_spi:type=232H -c MX25L1605A/MX25L1606E/MX25L1608E -r dump.bin”
The -p tells it we would like to use the ft2232 programmer (replace this with the -p argument above if using the Bus Pirate), the -c tells it what kind of flash chip we are working with that we would like to dump (in this case the MX25L1606E ), and -r dump.bin tells it to read the contents into the file dump.bin. If this completes successfully, we should get a valid firmware file. If it fails it will either error out completely or create a file filled with null bytes.
If you’re wondering how long this can take, it could be a while, especially with bigger chips. We can identify the size from the data sheet. The MX25L1606E ends at the address 1FFFFF which is 2097151 bytes or 2MB (fig.15).
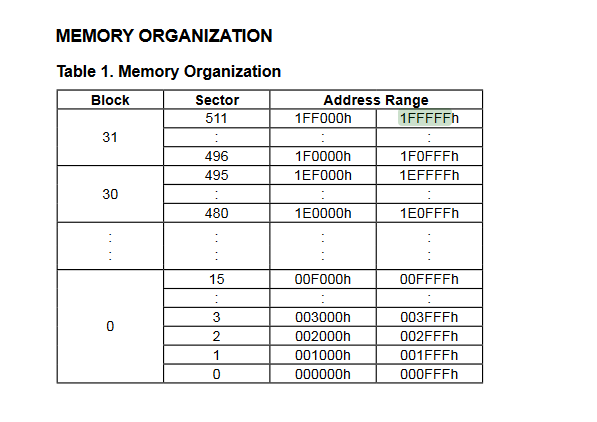
Figure 15 – mx25l1606e Memory Organization
This 2MB chip took about 2 minutes to fully dump. In the end, we are fortunate and get a successful firmware dump on the first try:
iot@attifyos ~> flashrom -p ft2232_spi:type=232H -c MX25L1605A/MX25L1606E/MX25L1608E -r dump.bin flashrom v0.9.9-r1954 on Linux 4.15.0-88-generic (x86_64) flashrom is free software, get the source code at https://flashrom.org Calibrating delay loop... delay loop is unreliable, trying to continue OK. Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L1605A/MX25L1606E/MX25L1608E" (2048 kB, SPI) on ft2232_spi. Reading flash... done.
Doing a binwalk presents the following:
iot@attifyos ~> binwalk dump.bin DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5440 0x1540 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 8388608 bytes, uncompressed size: 85344 bytes 28570 0x6F9A Sercomm firmware signature, version control: 256, download control: 0, hardware ID: "AAZ", hardware version: 0x3200, firmware version: 0x6, starting code segment: 0x0, code size: 0x7310 142352 0x22C10 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 8388608 bytes, uncompressed size: 2764800 bytes 881324 0xD72AC LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3450 bytes 882534 0xD7766 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 10162 bytes 884943 0xD80CF LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 118270 bytes 917640 0xE0088 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 11937 bytes 920834 0xE0D02 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2992 bytes 921709 0xE106D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 177 bytes 921863 0xE1107 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 116 bytes 921999 0xE118F LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 491 bytes 922337 0xE12E1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 718 bytes 922610 0xE13F2 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 20267 bytes 926110 0xE219E LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1196 bytes 926568 0xE2368 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 140 bytes 926729 0xE2409 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 708 bytes 927159 0xE25B7 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 17248 bytes 930471 0xE32A7 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 141 bytes 930632 0xE3348 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 543 bytes 930971 0xE349B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 4166 bytes 932391 0xE3A27 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 5883 bytes 933996 0xE406C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3257 bytes 935281 0xE4571 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 49 bytes 935337 0xE45A9 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 7205 bytes 936048 0xE4870 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 4716 bytes 937318 0xE4D66 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2506 bytes 937984 0xE5000 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 7376 bytes 938892 0xE538C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2951 bytes 939613 0xE565D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 7369 bytes 940273 0xE58F1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 11312 bytes 942619 0xE621B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 7671 bytes 944755 0xE6A73 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 300 bytes 945073 0xE6BB1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 99243 bytes 974918 0xEE046 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 89932 bytes 1006871 0xF5D17 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 55 bytes 1006939 0xF5D5B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1484 bytes 1007670 0xF6036 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 11316 bytes 1008768 0xF6480 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 6962 bytes 1010654 0xF6BDE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2723 bytes 1011701 0xF6FF5 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 9151 bytes 1013994 0xF78EA LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 13151 bytes 1016828 0xF83FC LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3592 bytes 1018079 0xF88DF LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 27452 bytes 1024437 0xFA1B5 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 711 bytes 1024870 0xFA366 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 71 bytes 1024953 0xFA3B9 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3861 bytes 1026104 0xFA838 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 4303 bytes 1026844 0xFAB1C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 11222 bytes 1029155 0xFB423 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2189 bytes 1030156 0xFB80C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 15453 bytes 1031493 0xFBD45 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 11326 bytes 1032515 0xFC143 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 4244 bytes 1036593 0xFD131 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 15755 bytes 1040878 0xFE1EE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2695 bytes 1042083 0xFE6A3 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1956 bytes 1043986 0xFEE12 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 6532 bytes 1045769 0xFF509 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 868 bytes 1046218 0xFF6CA LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2208 bytes 1047043 0xFFA03 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1010 bytes 1047474 0xFFBB2 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2793 bytes 1048685 0x10006D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1599 bytes 1049943 0x100557 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 49437 bytes 1055931 0x101CBB LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2276 bytes 1056907 0x10208B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 9850 bytes 1059309 0x1029ED LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 14359 bytes 1062254 0x10356E LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 115629 bytes 1096126 0x10B9BE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 142 bytes 1096289 0x10BA61 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2379 bytes 1097270 0x10BE36 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 9662 bytes 1099324 0x10C63C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 8110 bytes 1100452 0x10CAA4 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 16599 bytes 1104501 0x10DA75 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 113073 bytes 1139633 0x1163B1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 1164 bytes 1140114 0x116592 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2749 bytes 1141269 0x116A15 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 992 bytes 1141593 0x116B59 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2386 bytes 1142645 0x116F75 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3389 bytes 1143726 0x1173AE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2593 bytes 1144845 0x11780D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 112854 bytes 1178716 0x11FC5C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 23875 bytes 1182332 0x120A7C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 19256 bytes 1186345 0x121A29 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 22772 bytes 1189511 0x122687 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 19897 bytes 1193861 0x123785 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 5708 bytes 1195343 0x123D4F LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 118097 bytes 1230423 0x12C657 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2468 bytes 1231379 0x12CA13 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 122825 bytes 1264272 0x134A90 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 36 bytes 1264320 0x134AC0 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3331 bytes 1265332 0x134EB4 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 114489 bytes 1299549 0x13D45D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 6837 bytes 1301387 0x13DB8B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 13110 bytes 1303991 0x13E5B7 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 119 bytes 1304130 0x13E642 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3482 bytes 1305418 0x13EB4A LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2803 bytes 1306588 0x13EFDC LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 88006 bytes 1337278 0x1467BE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 6572 bytes 1339658 0x14710A LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2384 bytes 1342047 0x147A5F LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 141 bytes 1342210 0x147B02 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 73 bytes 1342295 0x147B57 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 856 bytes 1343170 0x147EC2 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 625 bytes 1343809 0x148141 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 183 bytes 1343969 0x1481E1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2619 bytes 1345099 0x14864B LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 3389 bytes 1346055 0x148A07 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 12586 bytes 1347838 0x1490FE LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 118 bytes 1347975 0x149187 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 650 bytes 1348652 0x14942C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2791 bytes 1349331 0x1496D3 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 615 bytes 1349749 0x149875 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 13284 bytes 1352395 0x14A2CB LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 4897 bytes 1353804 0x14A84C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 34279 bytes 1358905 0x14BC39 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 113 bytes 1359036 0x14BCBC LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 37989 bytes 1365372 0x14D57C LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2509 bytes 1366497 0x14D9E1 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 2175 bytes 1367477 0x14DDB5 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 7597 bytes 1369498 0x14E59A LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 5214 bytes 1371175 0x14EC27 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 43 bytes 1371229 0x14EC5D LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 114 bytes 1371363 0x14ECE3 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 290 bytes 1371584 0x14EDC0 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 65536 bytes, uncompressed size: 929 bytes
Looking at the line with “Sercomm Firmware Signature” we can see a hardware ID of “AAZ”, which matches the hardware ID on the board (fig.16). Now we can go ahead and analyze this firmware for vulnerabilities. Keep in mind, if we can dump firmware we can write custom firmware and backdoors to the flash chip as well.
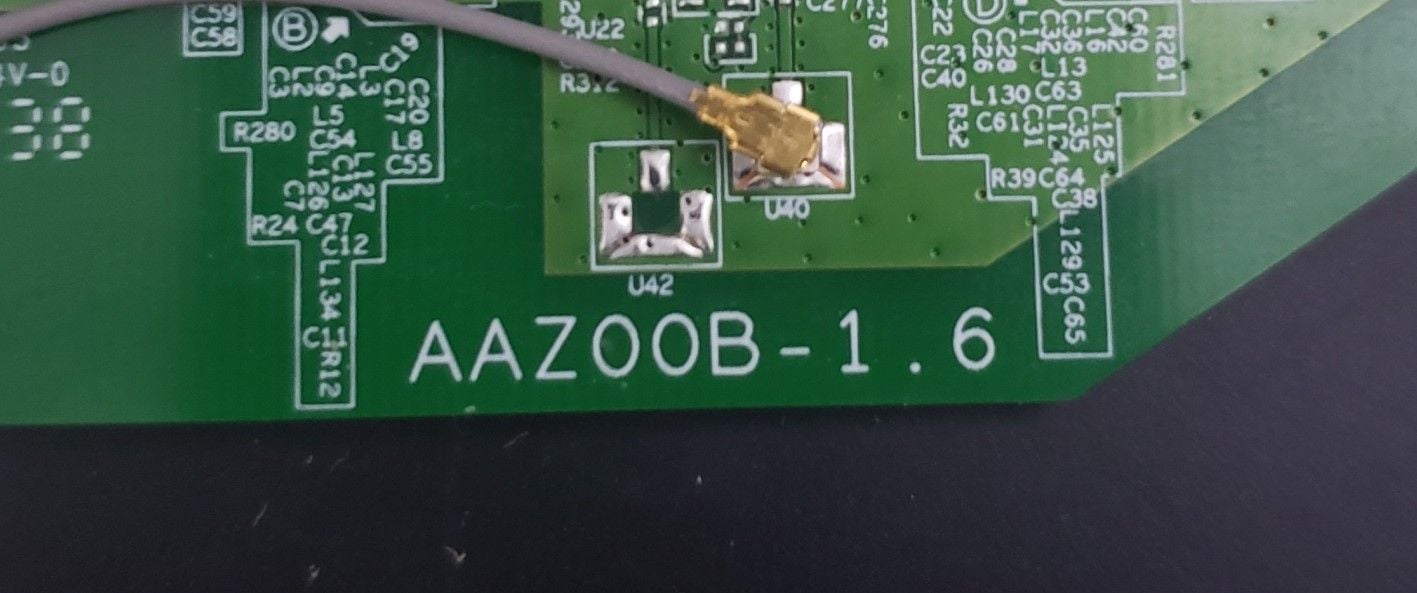

Figure 16 – Hardware Id
If anything fails, two of the most likely reasons are the pins aren’t properly connected or – if they are properly connected – it’s possible they are powering the SPI chip, which makes the chip inaccessible for dumping. The second scenario can be very common, and the best resolution generally is to simply de-solder the chip using a heat gun and dump the firmware with the chip on its own. As previously mentioned, it is worth checking the length of the cables to ensure the failure did not result from too long of cables.
While dumping these devices can take quite a bit of time, it gives us valuable insights into how these devices work. For example, by dumping the firmware for the Belkin device we can analyze the source web files directly – making it easier to identify remote vulnerabilities and exploits within the device. This also allows us to discover vulnerabilities that wouldn’t present themselves attacking the device blind.
By exploiting these types of devices, an attacker could create a backdoor within your router and reroute all your web traffic, stealing credentials for accounts such as your banking and ecommerce accounts. Knowing where these vulnerabilities exist gives us an opportunity to fix them before they can cause any significant damage.
In the next part of this series we will discuss JTAG and UART serial interfaces, how to access them, and what we can get out of them.
References:
Several tools were used to successfully dump these firmwares:
- SOIC Clip:https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B07R5LPTYM/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o04_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1
- A device for dumping firmware (Bus Pirate): https://www.amazon.com/SparkFun-PID-12942-Bus-Pirate/dp/B01KKYN9LW
- Cables and clips: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B083PRVPCR/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o03_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1
- SOIC Clip: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B07R5LPTYM/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o04_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1
- Additional useful wires: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B07PTYBFDT/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o00_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1
The Bus Pirate is used to interface with the SPI serial protocol to dump the firmware for us. Other viable alternatives include the Shikra (https://int3.cc/products/the-shikra) and the Attify Badge (https://www.attify-store.com/products/attify-badge-uart-jtag-spi-i2c-pre-soldered-headers). Each tool has its own advantages and disadvantages. The Bus Pirate is widely available and very well documented, making it the easiest to use in my opinion. The Shikra is considered to be far more stable and faster than the Bus Pirate but doesn’t have as much support. The Attify badge in comparison is far easier to setup in my experience but again has limited support. The Bus Pirate also provides a nice serial interface that allows you to easily communicate with the device manually if you’d like as well. I personally have one of each, as long as you have at least one of these you should be good to go, but the Shikra is considered more of a specialized tool so the Bus Pirate or the Attify badge are certainly a better place to start.
The cables and clips are pretty cheap and can be bought anywhere really, I recommend these specifically because they have provided me everything I need so far and clip on to the pins well.























